Instâncias Voláteis e Retentativas
Blocos Funcionais (FBs)
Os FBs possuem variáveis internas, que armazenam seus dados durante os ciclos consecutivos de execução. Conforme a necessidade da aplicação, estes FBs podem ter suas instâncias configuradas como retentivas (LOCAL_RETAIN ou GLOBAL_RETAIN) ou voláteis (LOCAL ou GLOBAL). As variáveis de entrada e saída associadas ao FB também podem ser configuradas como retentivas ou voláteis. As variáveis retentivas retêm seus valores após o desligamento do equipamento, enquanto as voláteis carregam seus valores iniciais após uma reinicialização.
Quando queremos que um FB mantenha os valores após a reinicialização do equipamento, é necessário que a instância do FB e as variáveis associadas às suas entradas sejam configuradas como retentivas. Isso fará com que as variáveis internas do FB e as variáveis de entrada associadas mantenham o valor anterior ao desligamento.
No exemplo abaixo temos a utilização do bloco TON (Temporizador de Habilitação em Atraso) com instância e variáveis retentivas:
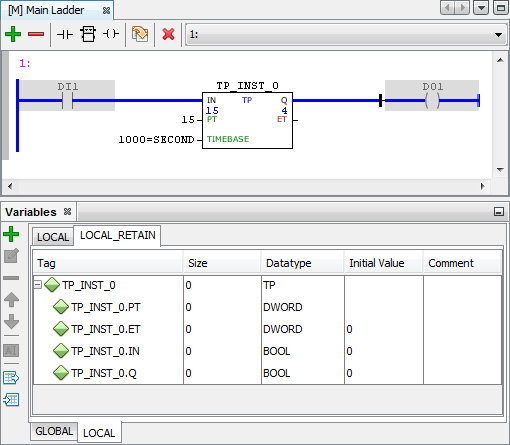
Figura 1 - Bloco TP com instância e variáveis retentivas antes da reinicialização.
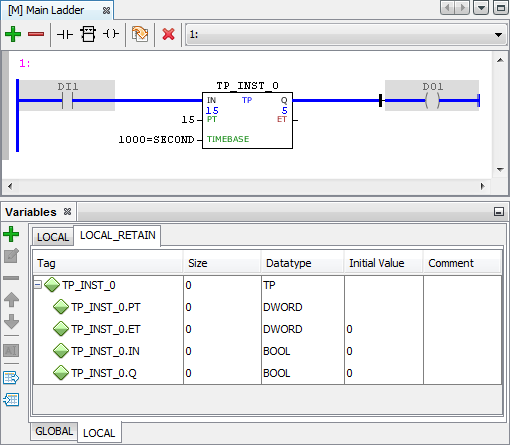
Figura 2 - Bloco TP com instância e variáveis retentivas 1 segundo após a reinicialização.
Quando queremos que um FB reinicialize seus valores após o desligamento do equipamento, é necessário que a instância do FB e as variáveis associadas às suas entradas sejam configuradas como voláteis. Isso fará com que as variáveis internas do FB e as variáveis de entrada associadas reinicializem o valor anterior ao desligamento.
Abaixo, segue um exemplo da utilização do bloco CTU (Contador Incremental) com instância e variáveis voláteis:
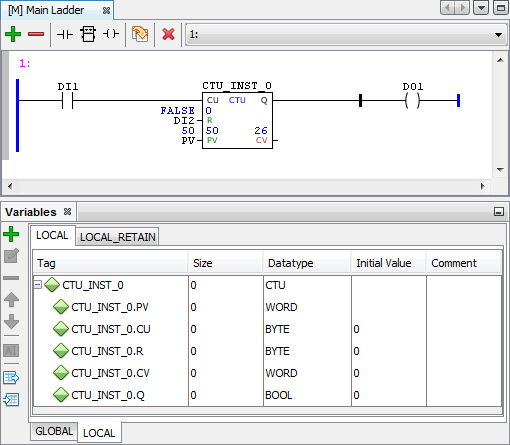
Figura 3 _ Bloco CTU com instância e variáveis voláteis antes da reinicialização.
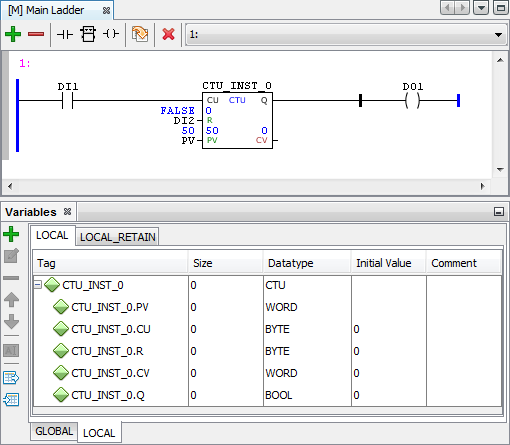
Figura 4 - Bloco CTU com instância e variáveis voláteis após a reinicialização.
Bloco do usuário (USERFB)
Na utilização do USERFB é possível definir variáveis do tipo LOCAL, LOCAL_RETAIN, VAR_IN, VAR_OUT e VAR_IN_OUT. As variáveis internas definidas como LOCAL serão sempre voláteis e as de tipo LOCAL_RETAIN serão sempre retentivas. As variáveis internas definidas como VAR_IN, VAR_OUT e VAR_IN_OUT serão voláteis caso a instância do USERFB seja associada ao grupo LOCAL ou GLOBAL e retentivas caso seja associada ao grupo LOCAL_RETAIN ou GLOBAL_RETAIN.