Block that performs a logical right rotation operation in a value passed by Value, storing the result in Result.
Ladder Representation

Block Structure
Variable Type |
Name |
Data Type |
Description |
VAR_INPUT |
EN |
BOOL |
Block enabling |
Value |
BYTE USINT SINT WORD UINT INT DWORD UDINT DINT |
Variable to undergo rotation |
|
Shift |
BYTE USINT |
Shift index |
|
VAR_OUTPUT |
ENO |
BOOL |
End of operation |
Result |
BYTE USINT SINT WORD UINT INT DWORD UDINT DINT |
Variable that stores the result of the operation |
Operation
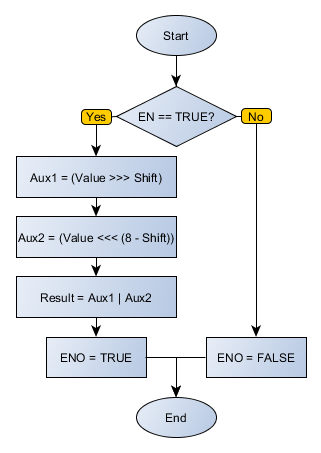
When this block has a TRUE value in EN, it sends to the Result output the value of the Value variable after performing a number of logical right shifts, according to the Shift value. The least significant bits that are being discarded are returned to the most significant bits, characterizing the rotation.
When EN has FALSE value, Result remains unchanged.
The ENO value forwards to the next Ladder block the EN value after the operation is completed.
Block Flowchart
Example in Ladder
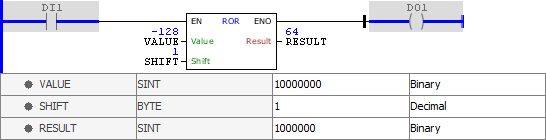
The above example performs a logic right shift by one position in the VALUE variable whose initial value is -128 (1000 0000 in binary). The discarded bits on the right are reinserted on the left. The final result (0100 0000 in binary) is stored in RESULT. Notice that the sign is not preserved in this operation.

The above example performs a logical right rotation by one position in the VALUE variable whose initial value is -127 (1000 0001 in binary). The discarded bits on the right are reinserted on the left. The final result (1100 0000 in binary) is stored in RESULT.
Example in ST
The example below displays the instructions for applying the example above in the ST language.
VAR VALUE : USINT := 2#1000_0001; SHIFT : BYTE := 1; RESULT : USINT; END_VAR
RESULT := FB_ROR( EN:=DI1, Value:=VALUE, Shift:=SHIFT, ENO=>DO1);
|
|---|